Setting up your epsSMASH job#
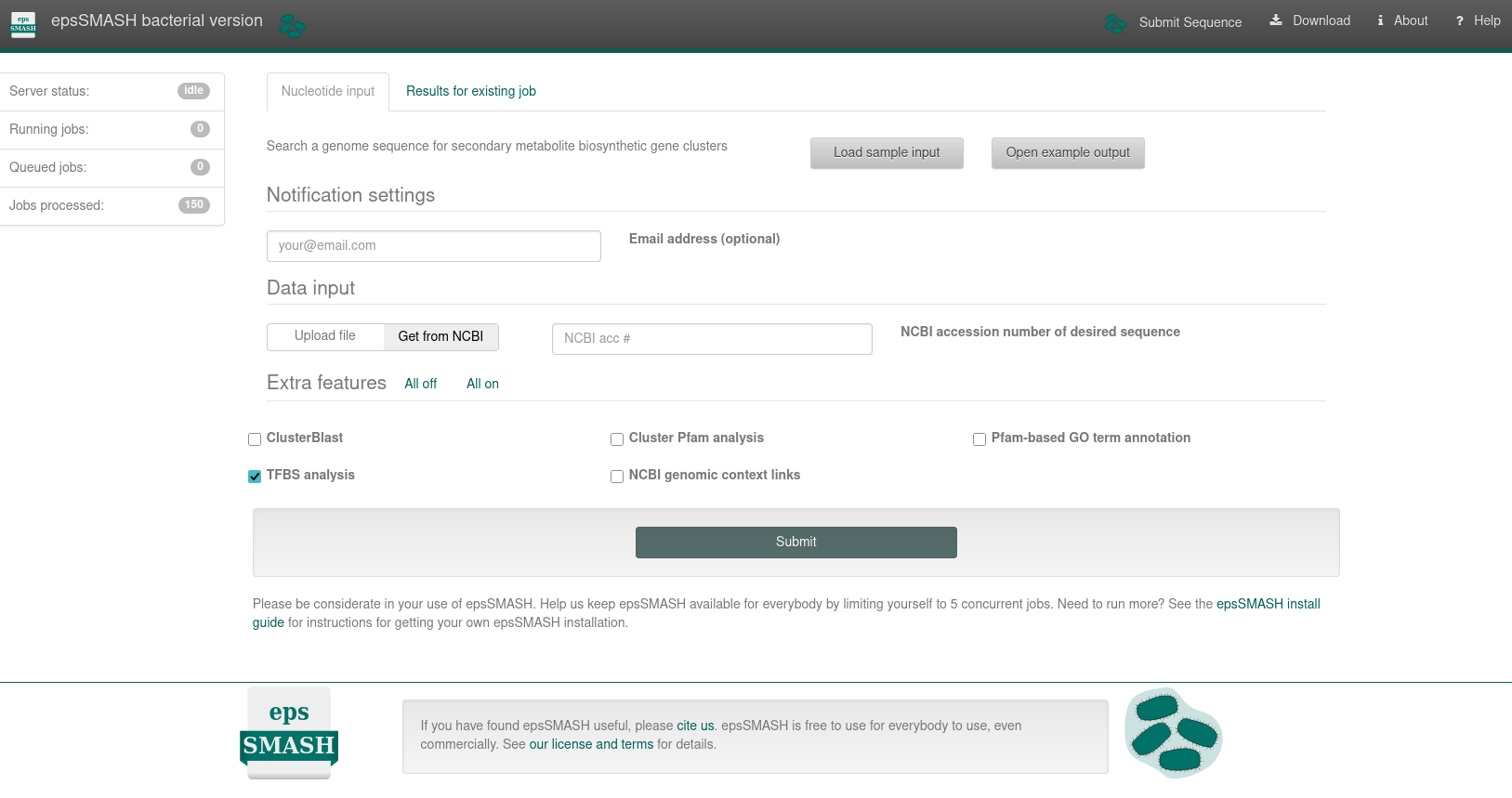
This page provides a comprehensive guide to obtaining interpretable output from the epsSMASH web server. It includes instructions on preparing the correct input data and explains the meaning of all settings and parameters required for the process. Here is the latest stable bacterial version of epsSMASH available, of which a screenshot is provided below:
Registering your epsSMASH job#
To receive an email notification upon job completion, you can provide your email address in the "Notification settings" panel. You'll get an email with a link to your results, or if there was an error. If no email is provided, remember to bookmark the job submission page, as you won’t be able to access the results later via the landing page.
epsSMASH input data#
The ideal input for epsSMASH is an annotated nucleotide file in Genbank format (.gbk, .gbff or .embl). You can toggle the option in the "Data input" panel where default is "Get from NCBI". With "Get from NCBI", epsSMASH will attempt to download the data directly from NCBI, based on the accession number provided.

In case no gene annotations are available for your sequence, we recommend running your sequence through an annotation pipeline like Prokka to obtain Genbank files with high-quality annotations. Alternatively, you can provide a FASTA file containing the contig(s) of a genome assembly. If you do this, epsSMASH will generate a preliminary annotation using Prodigal, and use that to run the rest of the analysis. You can also provide gene annotations in GFF3 format.
In any case, it is very important that input files are properly formatted. If you are creating your GBK/EMBL/FASTA file manually, be sure to do so in a plain text editor like Notepad or Emacs, and saving your files as "All files (.)", ending with the correct extension (for example ".fasta", ".gbk", or ".embl").
epsSMASH default and extra features#
Before pressing the submission button, you will have to indicate which epsSMASH features you would like to run.

Default epsSMASH features#
The following options are run by default if you do not toggle them off as can be seen in the screenshot from the "Extra features" panel:
TFBS Finder
TFBS Finder is a tool that searches for transcription factor binding sites (TFBS) in the BGCs detected by epsSMASH. The results can be viewed in the "TFBS Finder" tab of the HTML output, and the "TFBS Finder" sidepanel contains an overview of all the TFBS hits found in the region.
See TFBS Finder for more information.
Advanced epsSMASH features#
As can be seen in the screenshot above, all features can be easily toggled off or on in one click on the top of the "Extra features" panel. The following features are off by default and are considered to be useful for advanced users or in case interesting biosynthetic gene clusters were found that warrant further detailed analysis.
ClusterBlast analysis
The identified clusters are searched against a comprehensive gene cluster database based on manually validated exoPS gene clusters from epsProtocol, and similar clusters are identified. The algorithm used here is inspired by MultiGeneBlast. It runs BlastP using each amino acid sequence from a detected gene cluster as a query on a large database of manually validated exoPS gene clusters, and pools the results to identify the gene clusters that are most homologous to the gene cluster that was detected in your query nucleotide sequence. Please note that selecting this option increases the runtime significantly. The results are displayed in the "ClusterBlast" tab of the HTML output.
See ClusterBlast for more information.
Cluster Pfam analysis
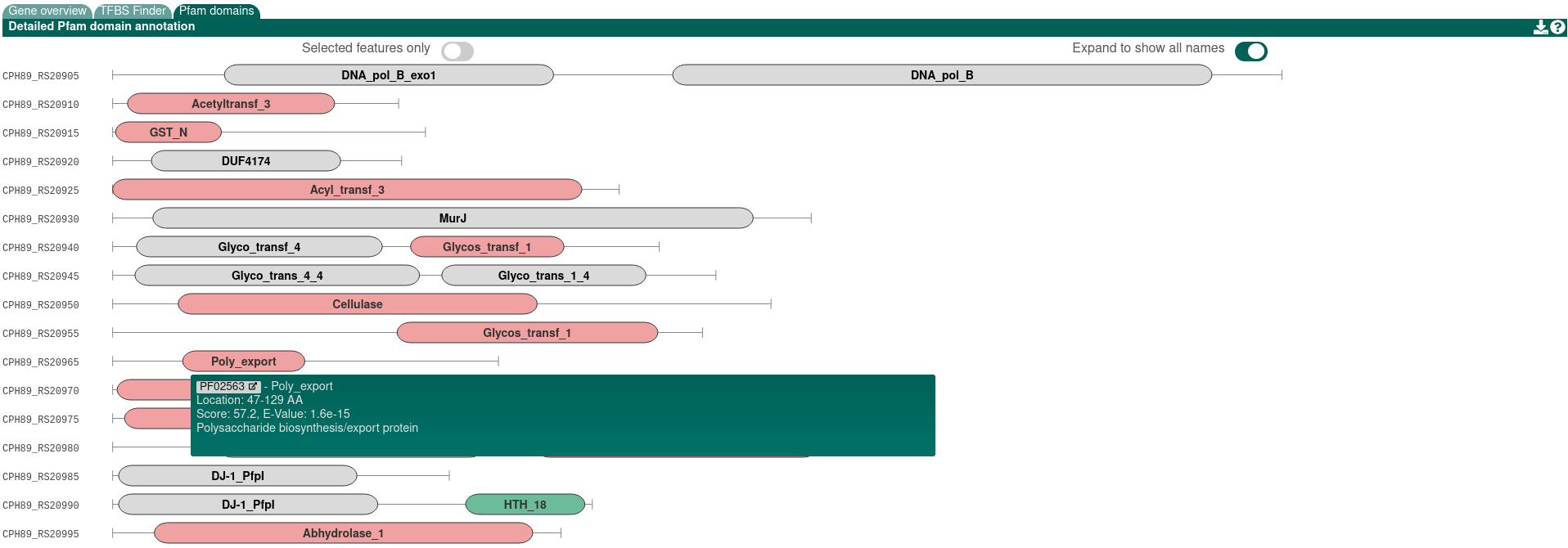
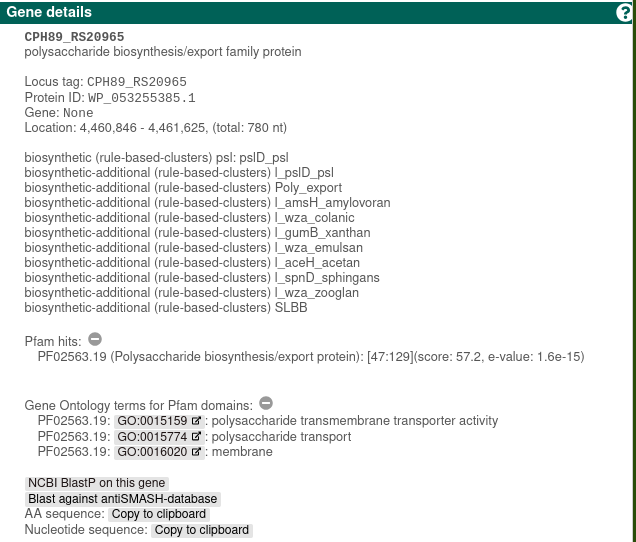
Each gene product encoded in the detected BGCs is analyzed against the PFAM database. Hits are annotated in the final Genbank/EMBL files that can be downloaded after the analysis is finished. Enabling this option will increase the runtime of a submission. The Pfam annotations are displayed in the HTML results in the "Pfam domains" tab. Additionally, Pfam details for a selected gene is shown in the "Gene details" sidepanel.

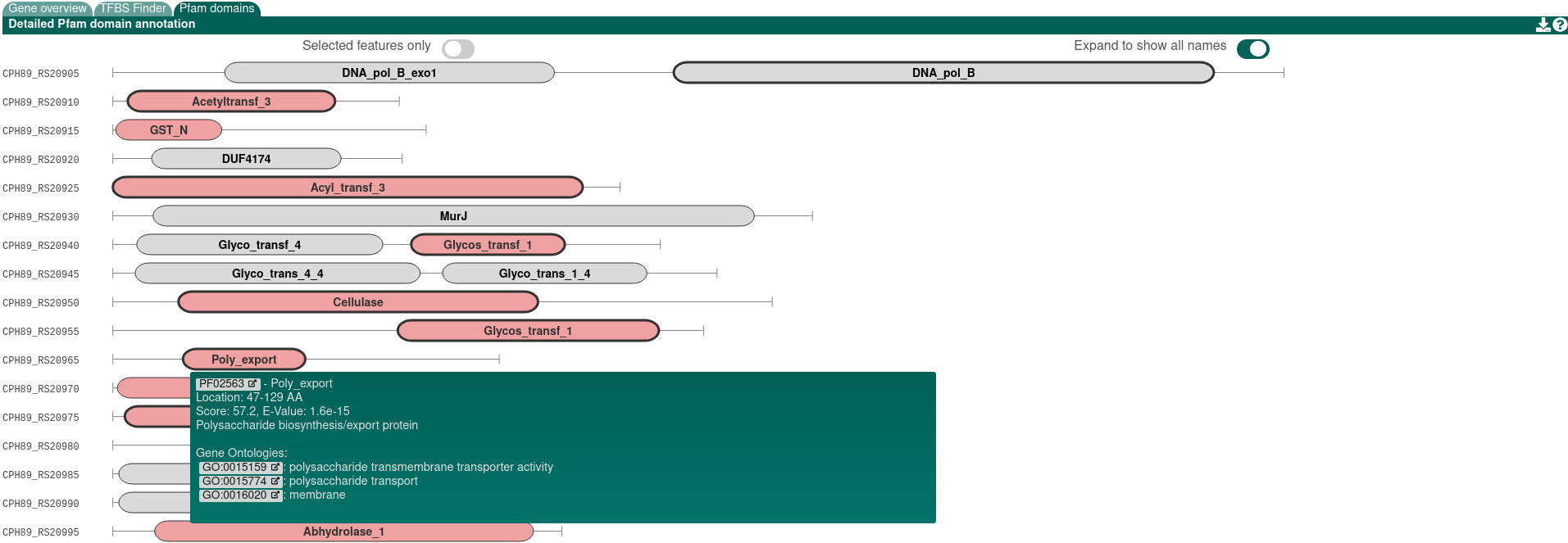
Pfam-based GO term annotation
This option annotates the results of the Cluster Pfam analysis, described above, with GO term annotations. These results are displayed within the Pfam domains section of the antiSMASH HTML results, by emphasising the borders of the relevant domains. Additionally, Pfam GO annotations for a selected gene is shown in the "Gene details" sidepanel beneath the Pfam details. See Understanding the output for instructions on how to download the results.
Submitting your query#
After you set up your online epsSMASH job, you can click on submit on the bottom of the page and the calculations for the identification and analysis of the gene clusters will be carried out on our servers. When the job is finished – and if an email address was provided – the user gets a notification email that the results are available. Otherwise, you will need to go to the bookmarked link to check if the analysis has finished.