HMM creation and rule building#
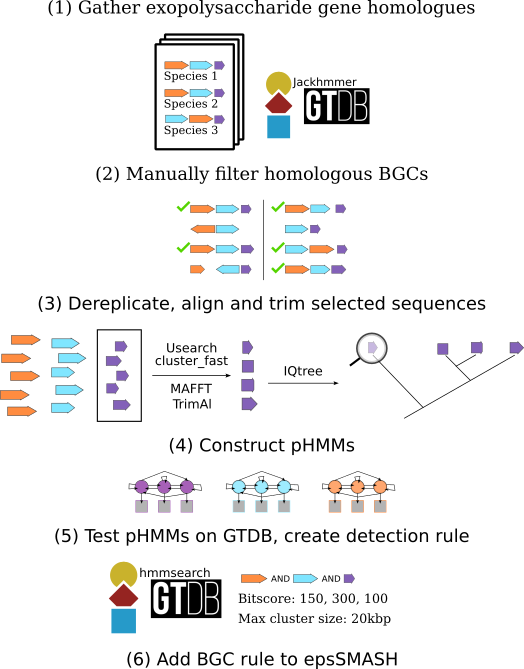
Most of the rules used in epsSMASH are created using a workflow we named epsProtocol. The epsProtocol is a multi-step process that combines literature knowledge with computational methods to create rules for detecting BGCs.
epsProtocol is described in short below. For an in-depth explanation of epsProtocol you can read the methods section of our paper
-
Amino acid sequences from a BGC described in literature (e.g. the alginate operon) are gathered and searched against all representative genomes in the Genome Taxonomy Database (GTDB) using Jackhmmer.
-
The resulting hits are grouped together into putative BGCs with any other hits within a 5000 bp radius of each other. Based on knowledge from literature, this collection of putative BGCs is filtered by specifying minimum amounts of genes in each cluster as well as the presence of core genes (e.g. at least 7 alginate genes of which two of them have to be the synthase complex, alg8 and al44). This filtered set of putative BGCs is then manually inspected to filter out any that do not resemble the BGCs described in literature of that type.
-
The genes from the filtered and manually inspected BGCs are dereplicated at 90% sequence similarity, aligned, trimmed and...
-
...finally used to build HMMs representing each gene in the BGC.
-
Before making an epsSMASH rule from the newly built HMMs, the HMMs are used to search all representative genomes in the GTDB. This is done in order to test their performance, and the results are used to inform the rule-making:
The GTDB hits are grouped together with any other hits within a 5000 bp radius of each other. The same filters as were used on the putative Jackhmmer BGCs (minimum genes, core genes) are then used on these putative BGCs, and the filtered BGCs are compared with the filtered and inspected validated BGCs. Often this comparison shows that the HMMs detects more BGCs than there are in the filtered and manually validated BGCs, and when manually inspected, these "new" clusters generally resemble those described in literature. In cases like this, the epsSMASH rule is identical to the minimum/core gene filter specified in the initial Jackhmmer analysis.
All HMMs in epsSMASH have their own bitscore cut-off, which is also decided based on the GTDB results. Bitscore cut-offs are selected to keep as many of the GTDB hits which were found to be in putative BGCs, while filtering out the ones which did not. Each epsSMASH rule also has a defined max cluster size (see region concept), which is set to the largest cluster size found in the GTDB hits plus some margin.
-
The rule is added to epsSMASH